The Difference Between the UK, Great Britain, and England
Exploring
4 mins read
Share

Updated at: 25 November, 2025
Published at: 26 February, 2019
By Allaa Ashraf
The Difference Between the UK, Great Britain, and England
Exploring
4 mins read

Updated at: 25 November, 2025
Published at: 26 February, 2019
By Allaa Ashraf
Share
The United Kingdom is one of the most interesting countries in the world and one of the most popular as well. Yet, some people get it mixed up with other countries, facts, and names that relate to it. When it comes to understanding the political and geographical divisions of the British Isles, it's easy to get confused by the terms UK, Great Britain, and England. Though they are commonly interchanged, they represent different entities that have their characteristics and meaning.
Let's delve into the complexities and shed light on the differences between these terms.
First things first, What is the British Isles?
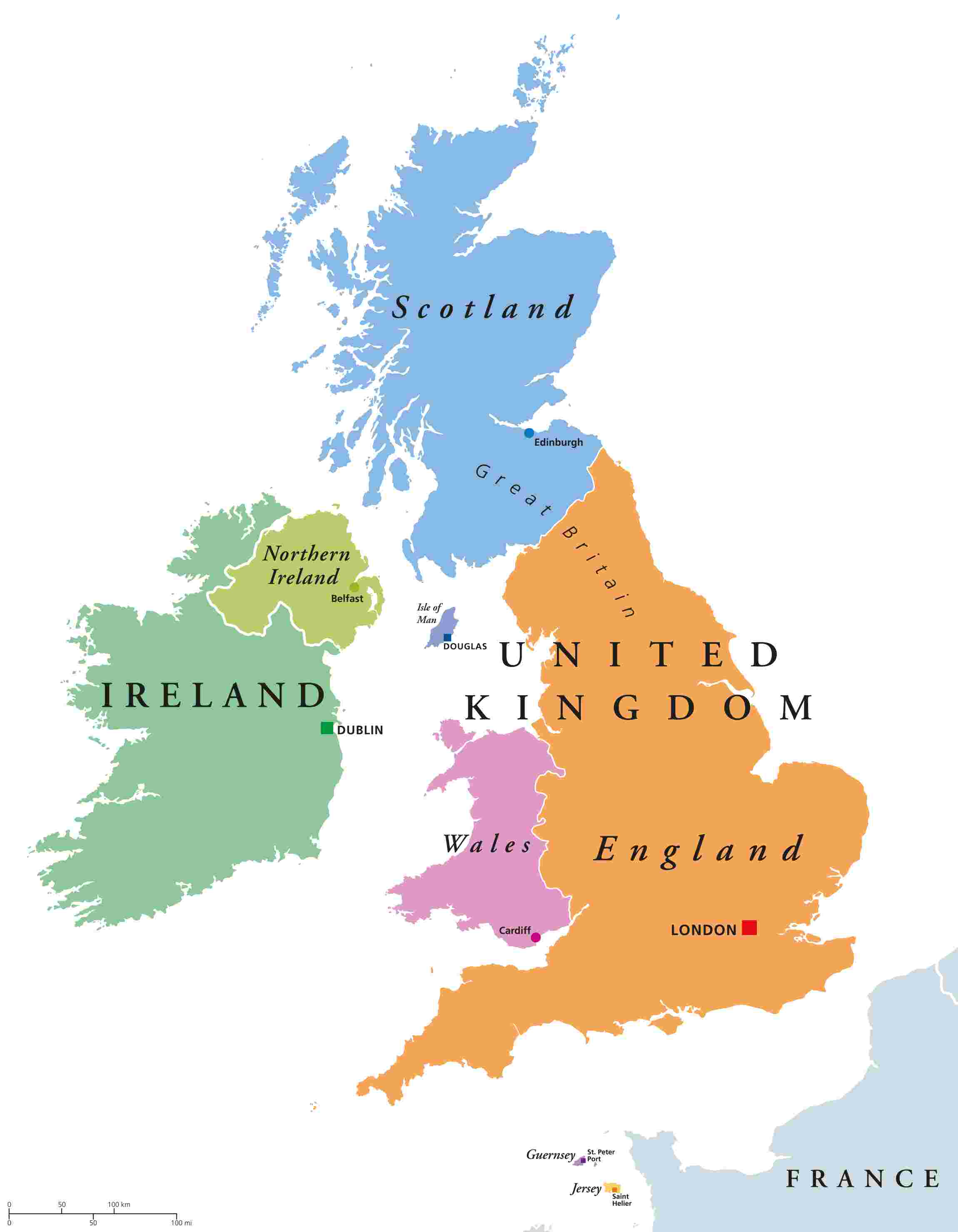
The British Isles is a geographical term that refers to a group of islands located off the northwestern coast of continental Europe. It encompasses not only the island of Great Britain but also Ireland, along with numerous smaller islands.
The term “British Isles” is purely geographical and does not have any political connotations. The British Isles countries are Scotland, England, Wales, Northern Ireland, and the Republic of Ireland.

Great Britain vs UK: How are the UK, Great Britain, and England Different?
1. The United Kingdom (UK)
The United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the UK, is a sovereign nation consisting of four constituent countries: England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. It is a political union formed in 1707 when the Kingdom of England, which included Wales, and the Kingdom of Scotland merged. In 1801, the Kingdom of Ireland joined the union, forming the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. However, in 1922, the Anglo-Irish Treaty led to the partition of Ireland, resulting in Northern Ireland remaining part of the UK while the rest of Ireland gained independence.
2. Great Britain (GB)
Great Britain refers to the largest island in the British Isles and is geographically comprised of three of the four constituent countries of the UK: England, Scotland, and Wales. It does not include Northern Ireland. Therefore, Great Britain is a purely geographical term, not a political entity.
3. England
England is one of the four constituent countries of the UK and occupies the southern and central parts of the island of Great Britain. It is the largest and most dominant nation in the UK. England possesses a unique identity, history, and legal system. The capital city of England and the UK, London, is a world centre of finances, culture, and politics.
Other Terms Related to the UK
Scotland
Another constituent country of the UK is Scotland and takes up the northern territory of the island of Great Britain. It possesses not only a specific legal system but also a system of education and cultural heritage. Scotland is a historical country with stunning landscapes, flourishing cities such as Edinburgh and Glasgow, and contribution to literature, science and arts.
Wales
Wales is also a constituent country of the UK and is located west to England. It has its own devolved government and a distinct cultural identity. Wales is famous for its stunning landscapes, such as the Snowdonia National Park, and rich Celtic culture.
Northern Ireland
The fourth member of the UK is Northern Ireland, located within the northeastern region of the island of Ireland. It is the state with a land border with Republic of Ireland and a complicated political history. Though Northern Ireland constitutes a part of the UK, there is a devolved government of Northern Ireland, and distinct cultural relationships.
Crown Dependencies and Overseas Territories
Besides the nations that constitute UK, other regions are also found to be related to British Isles. Crown Dependencies, including the Isle of Man, Jersey, and Guernsey (which includes the islands of Alderney, Sark, and Herm), have their own independent administrations and are not part of the UK but are under the sovereignty of the British Crown. They are autonomous to different extents and have their own laws.
The UK is known to have overseas territories as well that are distributed all over the world. They consist of such regions as Bermuda, Falklands, Gibraltar, and British Virgin Islands among others. They have great autonomy in self-governance, though they are under UK sovereignty and have different cultural identities.
Devolution
In the late 20th century, the UK underwent a process known as devolution, granting certain powers and decision-making authority to the devolved governments in Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland.
Devolution allows these regions to govern specific aspects of their internal affairs, such as education, health, and transportation, while certain areas, like defence and foreign affairs, remain under the control of the UK government.
During the late 20th century, UK experienced a process termed as devolution, which involved some powers and authority being given to the devolved governments located in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. Under devolution, such regions will take control of certain areas of its internal policy such as education, health, and transport sector while certain spheres, defence and foreign policy, will continue to be controlled by the UK government.
Union Jack and National Flags
The Union Jack is the official flag of the United Kingdom. It combines the flags of England (St. George's Cross), Scotland (St. Andrew's Cross), and Northern Ireland (St. Patrick's Cross). However, Wales is not represented on the Union Jack as it was considered part of the Kingdom of England when the flag was created.
Each constituent country within the UK also has its own distinctive national flag: the St. George's Cross for England, the St. Andrew's Cross (or Saltire) for Scotland, and the Red Dragon (Y Ddraig Goch) for Wales.
And there you have it!
We hope we managed to clear up some of the confusion around these terms, and you got to know the difference between Great Britain vs UK! Understanding these differences is crucial for appreciating the diverse identities and complexities of the British Isles. So, the next time you hear someone refer to the UK, Great Britain, or England, you can confidently navigate the distinctions and appreciate the unique attributes of each term.
Exploring
By Allaa Ashraf
Share
Exploring
Updated at:
Published at:
By Allaa Ashraf
Share


